Second Marking period
|
In the Beginning of the Second marking period, we will discuss how the United States formed a government after winning the Revolutionary War.
Creating a Nation
Constitution You Should know: Problems with the Articles of Confederation. Shays’ Rebellion Constitutional Convention
Articles of Confederation Shay’s Rebellion The Constitutional Convention Compromises Separation of Powers Ratification
|
The Constitutional Convention (1787)
Below is a chart detailing various issues that faced the framers of the constitution. The solutions that they created became the Constitution of the United States of America. Issue Compromise/Solutions Representation: 1. How would the legislature be chosen? The large states wanted representation based upon population; the smaller states wanted all states represented equally. 2. How would slaves be counted? The North wanted slaves counted for tax purposes, the south wanted slaves counted for the purposes of representation in Congress. 1. The Great Compromise: A bicameral legislature consisting of two houses was set up: a) The Senate: Upper House, all states represented equally, 2 per state. b) The House of Representatives: Representation by population. 435 members subject to change as per US census. 2. The 3/5 Compromise: Slaves were to be counted in the following manner; 5 slaves equaled three persons. Slavery: 1. Would slavery continue? 1. Yes, but the Constitutional convention banned importation of slaves after 1808. The Presidency: 1. How would the President be elected? 2. How long would the Presidents term of office be? 1. The Electoral College was created to vote for the President. Each state was given the same number of electors as they had representatives. In later years the Electoral college promised to vote based upon the what the majority of each state wanted. This became known as the electoral college promise. 2-- 4 Years. Power of the Federal Government 1. How would the powers of the states (something very important to the colonists who at that time felt more like "Virginians or Pennsylvanians" then Americans) be protected? 2. How would the central government's power be limited do that it could not take away peoples rights? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1. Federalism - The Federal system (also known as Division of Powers) was created. The federal government was given certain powers, the states were given certain powers and there were certain powers that they shared.
2. Checks and Balances: The government was divided into three branches. Each branch (Executive, Legislative and Judicial) was given certain powers that limited the powers of the other branches. In this way no one branch can gain too much power. This is also known as separation of powers.
The founding fathers also wrote the Bill of Rights.
These solutions and compromises formed the basis of the new American government written in a document called the Constitution of the United States.
2. Checks and Balances: The government was divided into three branches. Each branch (Executive, Legislative and Judicial) was given certain powers that limited the powers of the other branches. In this way no one branch can gain too much power. This is also known as separation of powers.
The founding fathers also wrote the Bill of Rights.
These solutions and compromises formed the basis of the new American government written in a document called the Constitution of the United States.
POWERS OF CONGRESS GAME
|
Powers of Congress Game- Each Student shall bring in a lunch bag size paper bag . In the bag should be eleven small, school appropriate items EACH of which symbolize one of the powers of congress enumerated in the constitution .
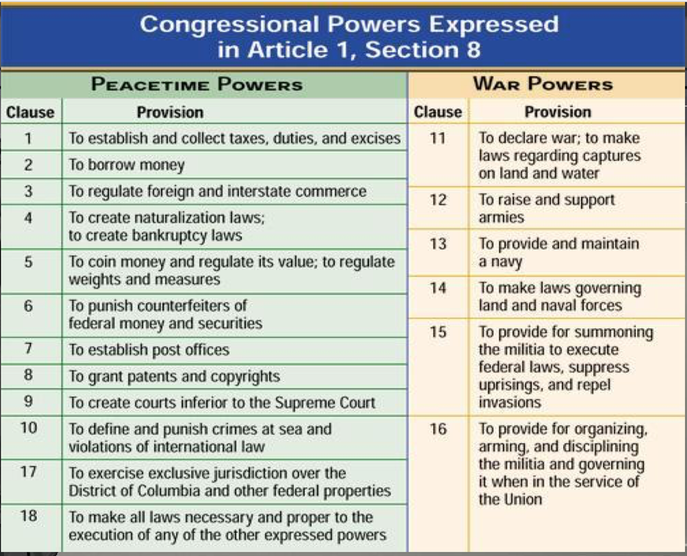
ENUMERATED POWERS: The Congress shall have Power To lay and collect Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises, to pay the Debts and provide for the common Defense and general Welfare of the United States; but all Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States; To borrow on the credit of the United States; To regulate Commerce with foreign Nations, and among the several States, and with the Native American Tribes; To establish a uniform Rule of Naturalization, and uniform Laws on the subject of Bankruptcies throughout the United States; To coin Money, regulate the Value thereof, and of foreign Coin, and fix the Standard of Weights and Measures; To provide for the Punishment of counterfeiting the Securities and current Coin of the United States; To establish Post Offices and Post Roads; To promote the Progress of Science and useful Arts, by securing for limited Times to Authors and Inventors the exclusive Right to their respective Writings and Discoveries; To constitute Tribunals inferior to the supreme Court; To define and punish Piracies and Felonies committed on the high Seas, and Offenses against the Law of Nations; To declare War, grant Letters of Marque and Reprisal, and make Rules concerning Captures on Land and Water; To raise and support Armies, but no Appropriation of Money to that Use shall be for a longer Term than two Years; To provide and maintain a Navy; To make Rules for the Government and Regulation of the land and naval Forces; To provide for calling forth the Militia to execute the Laws of the Union, suppress Insurrections and repel Invasions; To provide for organizing, arming, and disciplining, the Militia, and for governing such Part of them as may be employed in the Service of the United States, reserving to the States respectively, the Appointment of the Officers, and the Authority of training the Militia according to the discipline prescribed by Congress; To exercise exclusive Legislation in all Cases whatsoever, over such District (not exceeding ten Miles square) as may, by Cession of particular States, and the acceptance of Congress, become the Seat of the Government of the United States, and to exercise like Authority over all Places purchased by the Consent of the Legislature of the State in which the Same shall be, for the Erection of Forts, Magazines, Arsenals, dock-Yards, and other needful Buildings; And To make all Laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other Powers vested by this Constitution in the Government of the United States, or in any Department or Officer thereof. — Article I, Section 8 of the United States Constitution |
Take a small paper bag (lunch-bag size or smaller) and put at least 12 small, school appropriate items in it that represent 12 powers of Congress. Example: Congress has the power to make money - put a small coin in the bag.
On the due date, we will play the Powers Of Congress Game. Students will be divided into work groups. In each group, students will decide their best 12 items representing the Powers of Congress. If a students item is picked, that student receives 1 point in the game. In the Large Group, the class will vote on the best 12 items. If an item is chosen, each member of the group that submitted it will receive a game point. The student with the most points wins the game and receives a prize! If you show up to class without your items, you will be given an alternative assignment.
How does the Constitution give us a voice in Government?
As of 2015, there are 318.9 million Americans, so with 435 members of the House of Representatives, that gets you to 733,103 Americans/district. We in NJ have 12 Representatives in the House (see below). LODI is in the 5th NJ District and our Representative is Scott Garrett, Republican. He serves on the Budget and Financial Services Committees. But Mr. Garrett just lost an election this November, so after January, our Representative will be JOSH Gottheimer. Besides the House of Representatives ,each State gets 2 Senators. Since there are 50 States, there are 100 Senators. The two NJ Senators are Cory Booker and Robert Menendez, both Democrats. As of the 2010 Census, New Jersey has 14 electoral votes in a Presidential Election, representing 8.8 million people. That number comes from the amount of Representatives (12) and Senators (2, like every other state) from NJ. NJ House Members, Party, Phone Number, and Committee: 1Norcross, Donald D-202-225-6501Armed Services the Budget 2LoBiondo, Frank R-202-225-6572Armed Services Intelligence (Permanent) Transportation 3MacArthur, Tom R-202-225-4765Armed Services Natural Resources 4Smith, Chris R-202-225-3765Foreign Affairs 5Garrett, Scott R-202-225-4465Financial Services the Budget 6Pallone Jr., Frank D-202-225-4671Energy and Commerce 7Lance, Leonard R-202-225-5361Energy and Commerce 8Sires, Albio D-202-225-7919Foreign Affairs Transportation 9Pascrell Jr., Bill D-202-225-5751the Budget Ways and Means 10Payne Jr., Donald D-202-225-3436Homeland Security Small Business 11Frelinghuysen, Rodney R-202-225-5034Appropriations 12Watson Coleman, Bonnie D-202-225-5801Homeland Security Oversight and Government Select Panel | ||||||
QUIZ
| constitution_quiz_.pdf | |
| File Size: | 126 kb |
| File Type: | |
| constitution_million_game_1.ppt | |
| File Size: | 2966 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
DECEMBER
WEEK 5 -December 5-ish
CURRENT EVENTS DUE FRIDAY DEC 9th.
Chapter 6 Reading Checks Due Dec.13th
WEEK 5 -December 5-ish
CURRENT EVENTS DUE FRIDAY DEC 9th.
Chapter 6 Reading Checks Due Dec.13th
|
After the writing of the Constitution the nation began take form. As various issues arose political parties began to form around strong central leaders like Hamilton and Jefferson. In time the beliefs of these leaders became the beginning of the two party system.
Topics:
The Young Republic
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
THE era of good feelings - President James monroe
Homework
WEEK 6 -
Read Chapter 7 - Section 1 and 2 Reading Checks Due Friday January 6th.
Section 3 and 4 Reading Checks Due Friday January 13th. (End of Marking Period)
Chapter Terms (p. 262) Due Friday January 13th.
WEEK 6 -
Read Chapter 7 - Section 1 and 2 Reading Checks Due Friday January 6th.
Section 3 and 4 Reading Checks Due Friday January 13th. (End of Marking Period)
Chapter Terms (p. 262) Due Friday January 13th.
| us_1-_ch_7_8_student_teaching.doc | |
| File Size: | 66 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
| monroe_doctrine_and_the_era_of_good_feelings_[autosaved].pptx | |
| File Size: | 2249 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
| ch_7-_2_industry.ppt | |
| File Size: | 504 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
What changes took place in America during the Presidency of James Monroe?
What is the AMERICAN SYSTEM?
What is the AMERICAN SYSTEM?
THREE THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HENRY CLAY!!
1. He was a War Hawk during the War of 1812 along with J.C. Calhoun.
2. He was the Speaker of the House who devises the AMERICAN PLAN and pushed for John Q. Adams as President.
3. He was known as the Great Compromiser for the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850.
1. He was a War Hawk during the War of 1812 along with J.C. Calhoun.
2. He was the Speaker of the House who devises the AMERICAN PLAN and pushed for John Q. Adams as President.
3. He was known as the Great Compromiser for the Missouri Compromise and the Compromise of 1850.
| 09_-_early_republic_vocabulary_quiz.pdf | |
| File Size: | 331 kb |
| File Type: | |
| john_quincy_adams_as_president.ppt | |
| File Size: | 4137 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |