The economy and Politics
Economic Institutions
Capitalism- Entrepreneurs (people willing to risk money) control the means of production.
Law of Supply- Producers will supply more when they can charge a higher price. They will supply less when they can only command a lower price. How does this work for Pizza, Automobiles, or school bake sales?
Law of Demand- As prices lower, consumers will demand more of a product. As prices rise, consumers demand less. Think of how this works for this works for gasoline, silly-bands, baseball cards,School lunches etc.
Laissez-Faire-
Free-Enterprise-
Adam Smith-
Capitalism- The means of production is initiated and controlled by private individuals with their own money (capital).
Socialism- The Government or State Controls the means of production.
Not the same as Communism, but for many, the goal of socialism is communism. For Capitalists, the nightmare is communism.
Communism- The Government controls ownership of property for the purpose of fair distribution.
Totalitarianism- a system of government that is centralized and dictatorial and requires complete subservience to the state.
Authoritarianism -,the enforcement or advocacy of strict obedience to authority at the expense of personal freedom.
Corporate Capitalism- a capitalist marketplace characterized by the dominance of hierarchical and bureaucratic corporations.
Law of Supply- Producers will supply more when they can charge a higher price. They will supply less when they can only command a lower price. How does this work for Pizza, Automobiles, or school bake sales?
Law of Demand- As prices lower, consumers will demand more of a product. As prices rise, consumers demand less. Think of how this works for this works for gasoline, silly-bands, baseball cards,School lunches etc.
Laissez-Faire-
Free-Enterprise-
Adam Smith-
Capitalism- The means of production is initiated and controlled by private individuals with their own money (capital).
Socialism- The Government or State Controls the means of production.
Not the same as Communism, but for many, the goal of socialism is communism. For Capitalists, the nightmare is communism.
Communism- The Government controls ownership of property for the purpose of fair distribution.
Totalitarianism- a system of government that is centralized and dictatorial and requires complete subservience to the state.
Authoritarianism -,the enforcement or advocacy of strict obedience to authority at the expense of personal freedom.
Corporate Capitalism- a capitalist marketplace characterized by the dominance of hierarchical and bureaucratic corporations.
Political Institutions
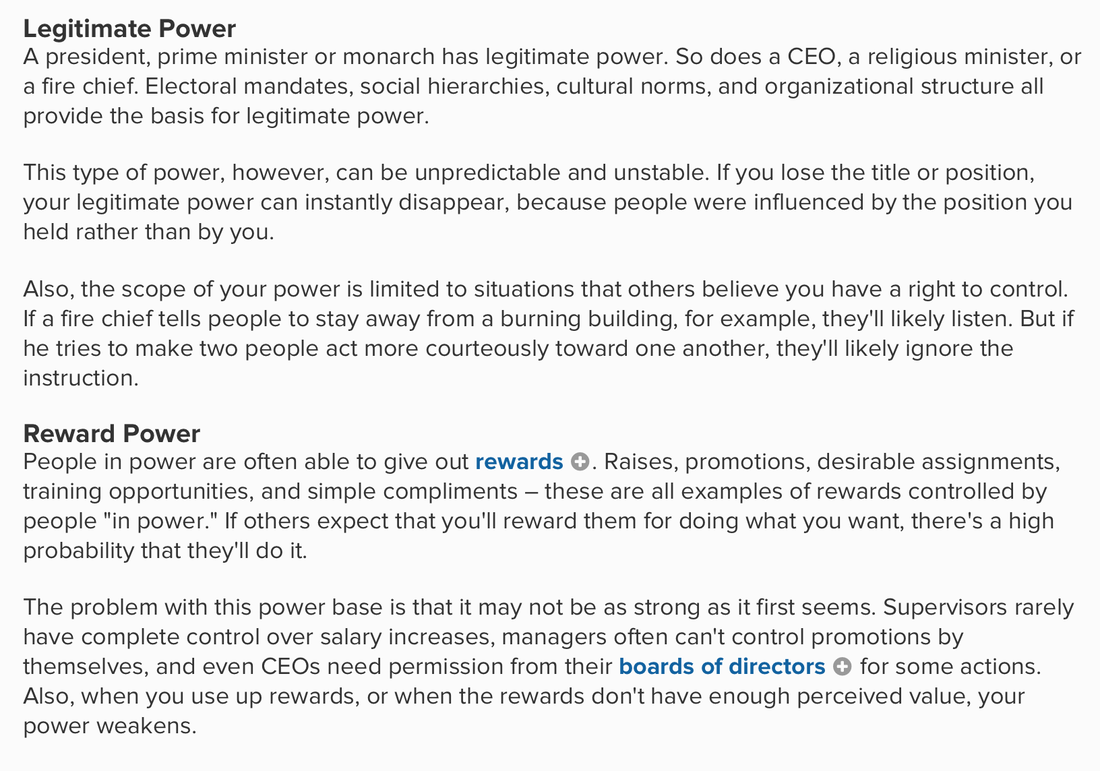
-Democracy- a system of government by the whole population or all the eligible members of a state, typically through elected representatives.
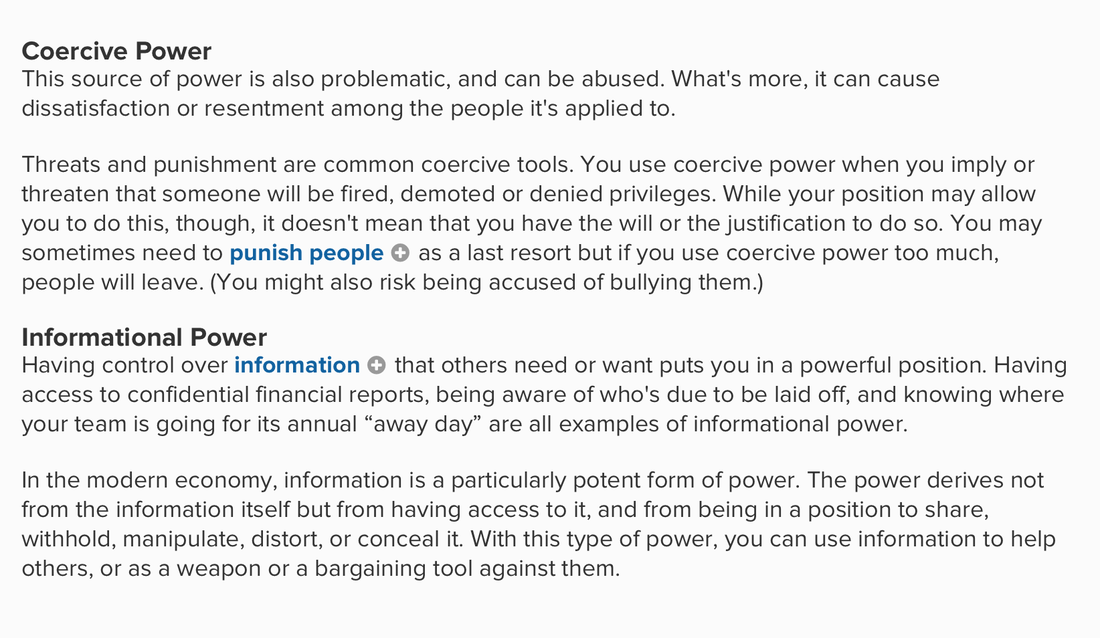
Monarchy- a form of government with a monarch at the head. ( The rule of one). Oligarchy- a small group of people having control of a country, organization, or institution. Authority- In sociology, authority is the legitimate power which one person or a group possesses and practices over another. ... Power can be exerted by the use of force or violence. Authority, by contrast, depends on the acceptance by subordinates of the right of those above them to give them orders or directives. Coercion- The word coercion means 'force'. It is the practice of getting people to fall in line with what one wants through the use of force, threat, fear, or punishment. In a broader sense in sociology, the term 'coercion' would be applied in the context of social order. Democratic Systems Authoritarian Systems Political Parties Proportional Representation - an electoral system in which parties gain seats in proportion to the number of votes cast for them. Who Rules America? Power Elite - The Power Elite is a 1956 book by sociologist C. Wright Mills, in which Mills calls attention to the interwoven interests of the leaders of the military, corporate, and political elements of society and suggests that the ordinary citizen is a relatively powerless subject of manipulation by those entities. Pluralism- a condition or system in which two or more states, groups, principles, sources of authority, etc., coexist. Instrumental vs. Expressive Leadership - Many of us choose to be in social groups because there are number of benefits that we receive as members. We may choose to be in a group for instrumental (or task) reasons so that the other group members can help us accomplish something. Or, we may choose to be in a group for expressive (or emotional) reasons so that the other group members can provide us with companionship, love, and security. Think about our social groups in the context of leadership. There are typically two types of leadership: instrumental and expressive. Instrumental leadership focuses on achieving goals. Leaders who are dominantly instrumental work to maintain productivity and ensure that tasks are completed. They make good managers because they get the job done. However, they are often so focused on the task that they can alienate other members of the group. Expressive leadership, on the other hand, focuses on maintaining group cohesion. Leaders who are dominantly expressive work to maintain warm, friendly relationships and ensure the collective well-being of the group. They make good bosses because they truly care for their employees. However, they are sometimes lacking efficiency and organizational skills. Although most leaders are dominantly instrumental or expressive, both styles are needed for groups to work effectively. So, the most effective leaders have the ability to use the style that best fits the situation. They can switch from being instrumental and focusing on the task, to being expressive and focusing on collaboration, whenever they see a need. |